The change in the U.S. government is dramatically reshaping cryptocurrency regulation. According to the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), nearly 60% of recent enforcement cases have targeted crypto companies.
At the same time, a growing number of these cases have been rejected or stopped, marking a sharp departure from the aggressive posture of recent years. In parallel, Donald Trump is preparing to appoint a new Federal Reserve chair who supports rate cuts, reinforcing expectations of a looser financial environment.
Together, these developments are creating a new paradigm for digital assets in the world’s largest economy.
The american regulatory revolution
Changes in the U.S. approach to cryptocurrencies have exceeded even the industry’s most optimistic expectations. According to the SEC, the majority of rejected or stopped enforcement actions involve crypto companies, a share significantly higher than the dismissal rate in other regulatory areas.
Among the dropped investigations were high-profile lawsuits against Ripple Labs and Binance, cases that had long symbolized regulatory hostility toward the sector.
This regulatory softening is not limited to enforcement alone. In parallel, the Senate approved the appointment of two cryptocurrency advocates to key regulatory positions. Mike Selig has been appointed head of the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC), while Travis Hill has taken over leadership of the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC).
Both appointments were met with a positive reaction from the industry, as each official has previously demonstrated a pragmatic and relatively friendly stance toward digital assets.
Political signals are reinforcing this shift. Trump has also narrowed the list of candidates for Federal Reserve chair to four individuals, singling out Christopher Waller as “magnificent”. According to Polymarket, cryptocurrency-supporting economist Kevin Hassett currently leads the odds, with a 53% chance of securing the position.
Markets are increasingly interpreting these signals as confirmation that regulatory and monetary policy may soon align more favorably with risk assets, including crypto.
Bitcoin in search of direction
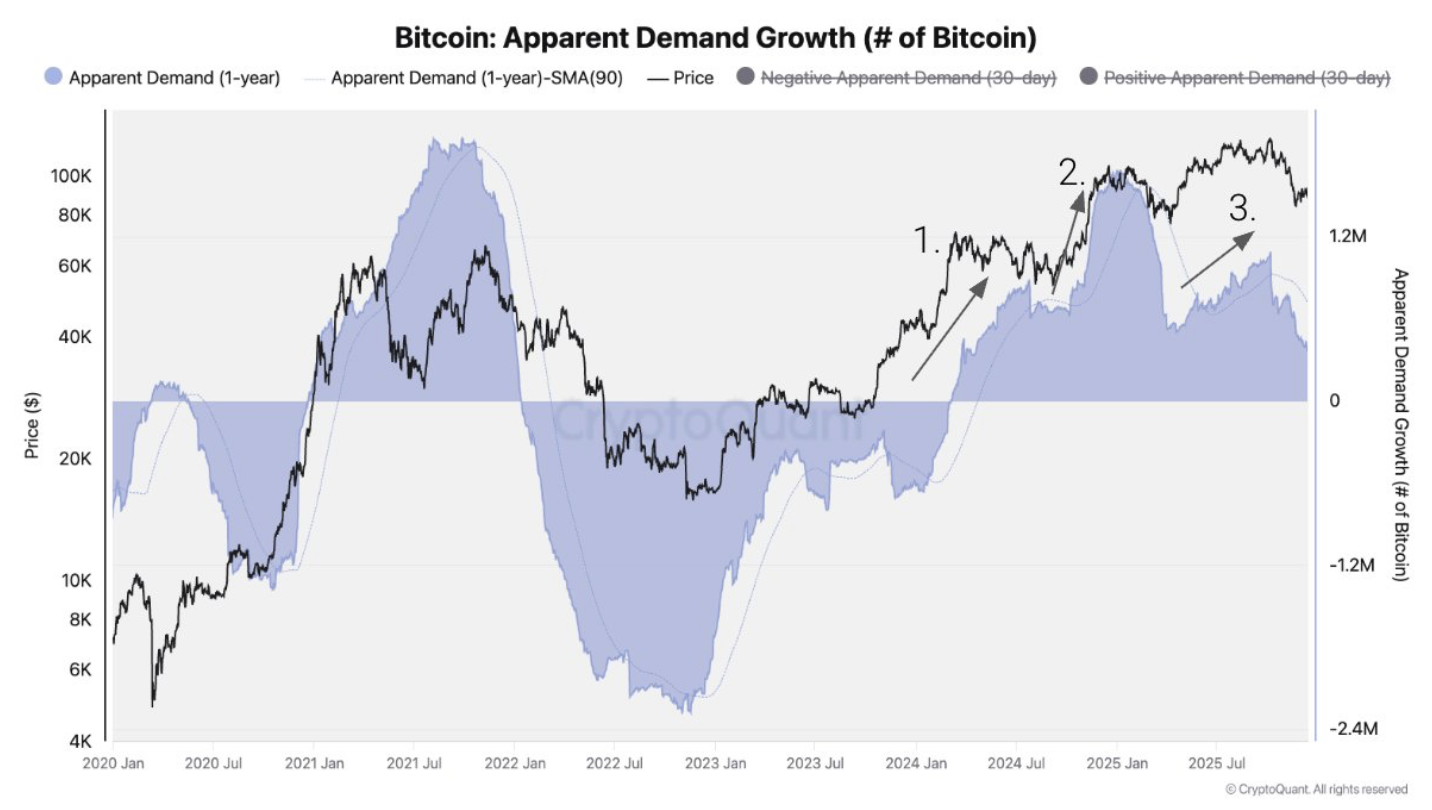
Despite the improving regulatory backdrop, Bitcoin itself is struggling to regain momentum. CryptoQuant analysts have declared the start of a bear market, pointing to a sharp decline in demand since October. According to their analysis, three major demand waves: the launch of spot ETFs, the U.S. elections, and corporate Bitcoin acquisitions have largely exhausted their short-term impact.
Bitcoin Demand Dynamics. Source: CryptoQuant
Large holders have added to the pressure. Over the past weeks, whales arranged sales totaling roughly $2 billion, including significant outflows from Binance (4,173 BTC), Coinbase (2,370 BTC), and BitMEX (7,516 BTC). As a result, Bitcoin has been trading in a tight $84,200-$93,500 range for several weeks, repeatedly failing to break higher.
However, signs of renewed institutional interest are emerging beneath the surface. Bitcoin ETFs recorded net inflows of $450 million last week, the strongest performance in a month. Fidelity led the inflows with $391 million, suggesting that long-term allocators continue to view recent weakness as an accumulation opportunity.
Grayscale analysts, meanwhile, maintain their forecast that Bitcoin could reach a new all-time high by the first half of 2026.
This tension between short-term exhaustion and long-term optimism has defined crypto market sentiment throughout the week.
The AI revolution requires the energy of entire cities
While crypto markets consolidate, another force is reshaping the global resource landscape. Artificial intelligence has become a major consumer of planetary resources. Research indicates that by 2025, AI could become the world’s most resource-intensive technological sector.
Its carbon footprint is already estimated to match that of New York City, producing between 32.6 and 79.7 million tons of CO₂ annually.
Global AI energy consumption has reached 23 gigawatts, surpassing the total energy use of Bitcoin mining. At the same time, AI systems consume between 312.5 and 764.6 billion liters of water per year,comparable to the annual consumption of the entire global bottled water market.
In regions surrounding major data centers, wholesale electricity prices have increased by as much as 267% over the past five years.
Geopolitical transformation of finance
Against this backdrop, global central banks are accelerating a shift away from traditional dollar dependence. Record gold purchases reflect a broader dedollarization trend. Regulators increased gold acquisitions by 28% in the third quarter, purchasing a total of 220 tonnes.
Notably, 66% of these purchases were not recorded in official IMF statistics, raising concerns about transparency and hidden reserve accumulation.
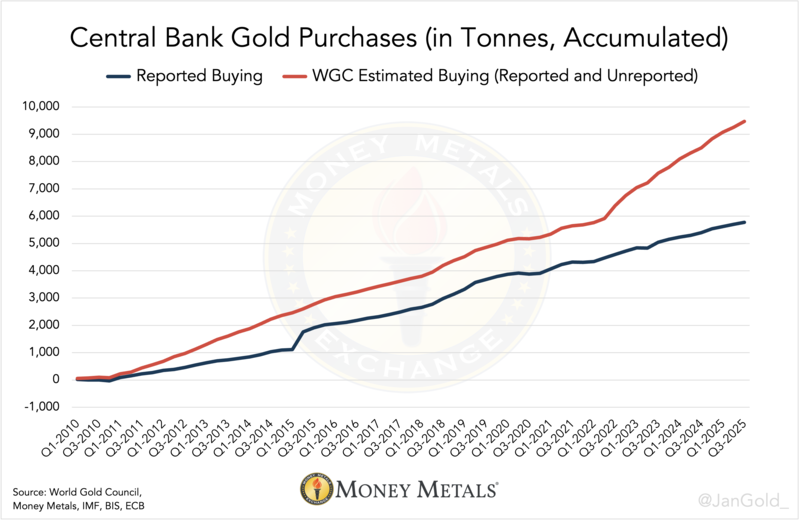
Central bank gold purchases reveal a huge gap between official data and expert estimates. Source: Money Metals
Independent estimates suggest that China is quietly building gold reserves that could exceed 5,000 tonnes, double the officially reported figure. The People’s Bank of China disclosed purchases of just five tonnes in the third quarter, bringing reported reserves to 2,303 tonnes, but analysts believe the true numbers are significantly higher.
Technological sovereignty as a new battlefield
Technology policy is increasingly intersecting with geopolitics. U.S. sanctions have created a multibillion-dollar domestic market for AI chips in China. Shares of MetaX Integrated Circuits surged 693% on their first trading day, raising nearly $600 million, while Nvidia’s share of the Chinese AI accelerator market has fallen from 95% to nearly zero.
Experts warn that digital sovereignty will define the next generation of global leaders. Countries must retain control over cryptography and digital identity systems; without this, they risk losing sovereignty over data, AI infrastructure, and long-term strategic autonomy.
Looking ahead, quantum computing is expected to break much of today’s cryptography between 2030 and 2035, forcing a fundamental rethinking of blockchain and AI security architectures.
Source:: This Week in Crypto: The Regulatory Turn, AI Energy Shock, and the Global Repricing of Power