Key highlights:
- OpenAI surpassed $20 billion in annual revenue in 2025, tripling its revenue from the previous year.
- The Sora video generator costs over $5 billion per year, putting significant pressure on profits.
- GPT-5 failed to meet user expectations, and mass departures of key staff add to operational risks.
OpenAI reached annual revenue exceeding $20 billion by 2025, tripling the previous year’s figure. The company’s CFO, Sarah Friar, officially announced the record results on January 19.
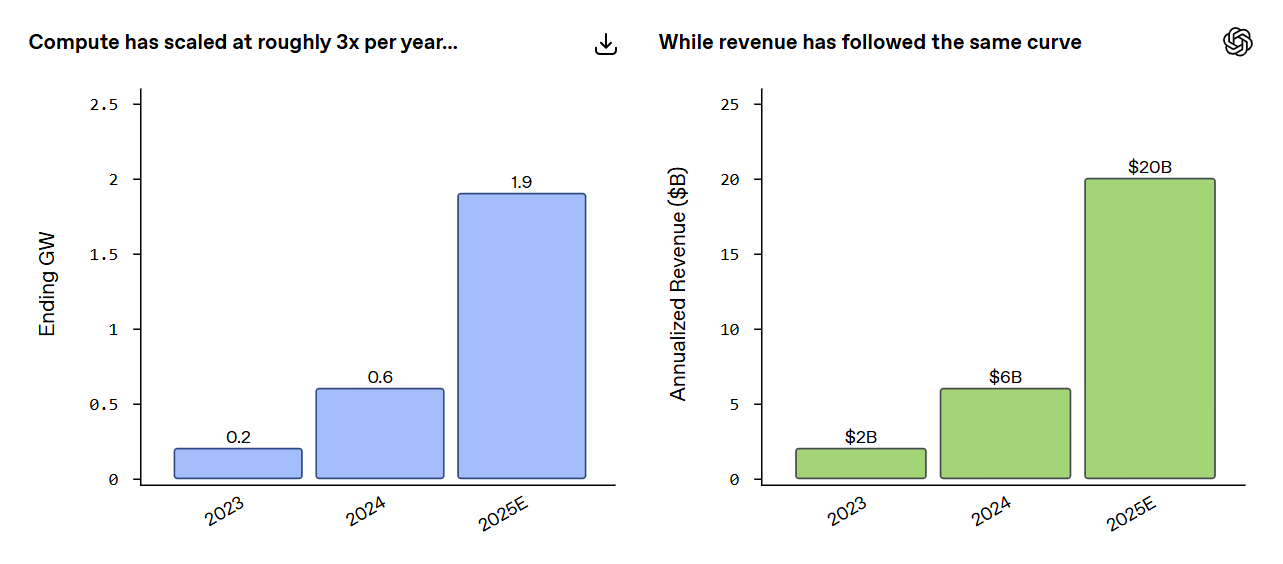
Rapid revenue growth was accompanied by a massive expansion of computing capacity. While the company had 0.2 GW in 2023, by 2025 this had grown almost tenfold to 1.9 GW, providing the infrastructure needed to support the company’s growth.
Source: OpenAI compute vs revenue
High costs of Sora challenge profits
Despite impressive revenue figures, the costs of developing the Sora video generator threaten profitability. According to Forbes, OpenAI spends up to $15 million per day on video generation, totaling over $5 billion annually.
Sora lead engineer Bill Peebles admitted last October that the project’s economic model was “completely unsustainable.”
rate limits for everyone are unchanged right now (pro users get 100/day, everyone else gets 30/day). we will need to increase the gens/day used by sora 2 pro to make the economics work out (video models really are expensive!), but we’re easing into it
— Bill Peebles (@billpeeb) October 31, 2025
Internal reports indicate that improving model quality requires exponentially higher resources: doubling quality demands a fivefold increase in energy consumption and operating costs.
GPT-5 underwhelms users and staff departures increase risk
The launch of GPT-5 did not meet user expectations, with widespread criticism over issues in mathematics and geography. Subsequent versions, GPT-5.1 and GPT-5.2, failed to fully resolve these flaws. VentureBeat described the rollout as “not going smoothly.”
2025 also saw a mass exodus of top staff, including CTO Mira Murati, Chief Scientist Ilya Sutskever, and President Greg Brockman, along with half of the security team. Dissatisfaction with CEO Sam Altman’s management style contributed to these departures, increasing operational risks for the company.
Legal challenges and ambitious goals
OpenAI faces a legal challenge from Elon Musk, who filed a lawsuit demanding $134 billion in compensation related to the company and Microsoft. Musk is seeking a share of OpenAI’s current $500 billion valuation. Attempts to dismiss the case were rejected, with trial scheduled for April 2026.
Looking ahead, OpenAI aims to reach $200 billion in annual revenue by 2030, requiring 15-fold growth amid rising costs. CEO Sam Altman has cautioned that investors may be “overly excited” about AI, warning that “someone is going to lose a lot of money.”
Market outlook
OpenAI’s financial trajectory mirrors tech giants of the 2000s and 2010s: massive upfront investments followed by delayed profits. Modern AI models, however, require exponentially growing computing resources, creating new economic dynamics.
The analysis highlights a paradox: the more successful a product like Sora becomes, the more it consumes profits. This may drive innovation in neural network efficiency or reveal fundamental scaling limits. The key question remains whether the AI services market can generate sufficient value to justify these investments.
Source:: OpenAI Generated $20B Revenue in 2025 but Faces Rising Economic Threats